Introduction to Unix shell in Azure
Part 1
Have a go at using these basic commands.
Try and apply them to these exercises.
Part 2
This goes further into more advanced commands and how to create shell scripts, which you need for running jobs.
Try and apply them to these exercises.
Batch Jobs in Azure
Read about batch jobs here.
Create a Batch Account
Search batch account in Search resources, services and docs.
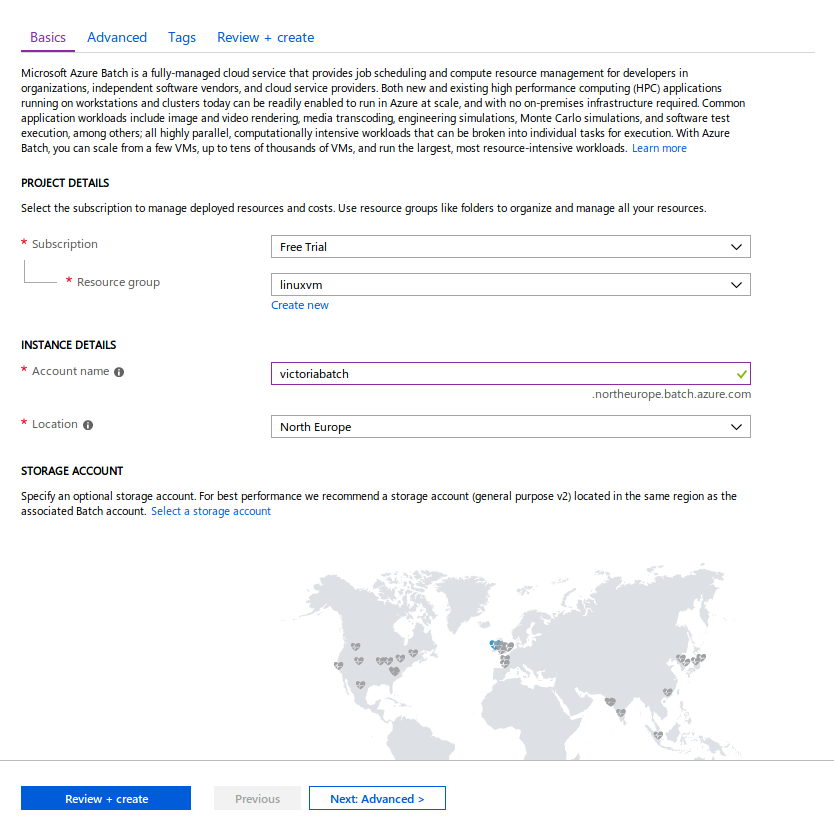
In Basics, select linuxvm in Resource group and create an Account name in North Europe.
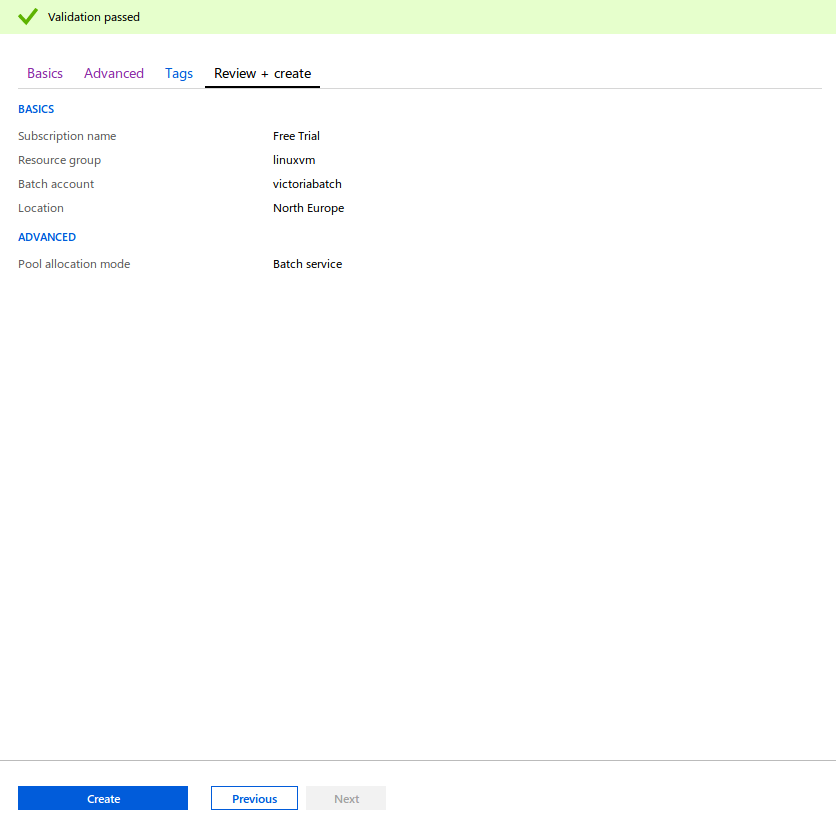
In Advanced, keep default option to Batch service.
In Tags, add Workshop in NAME and Linux in VALUE.
In Review + create, once Validation has passed, click Create. This should deploy in about 30 seconds.
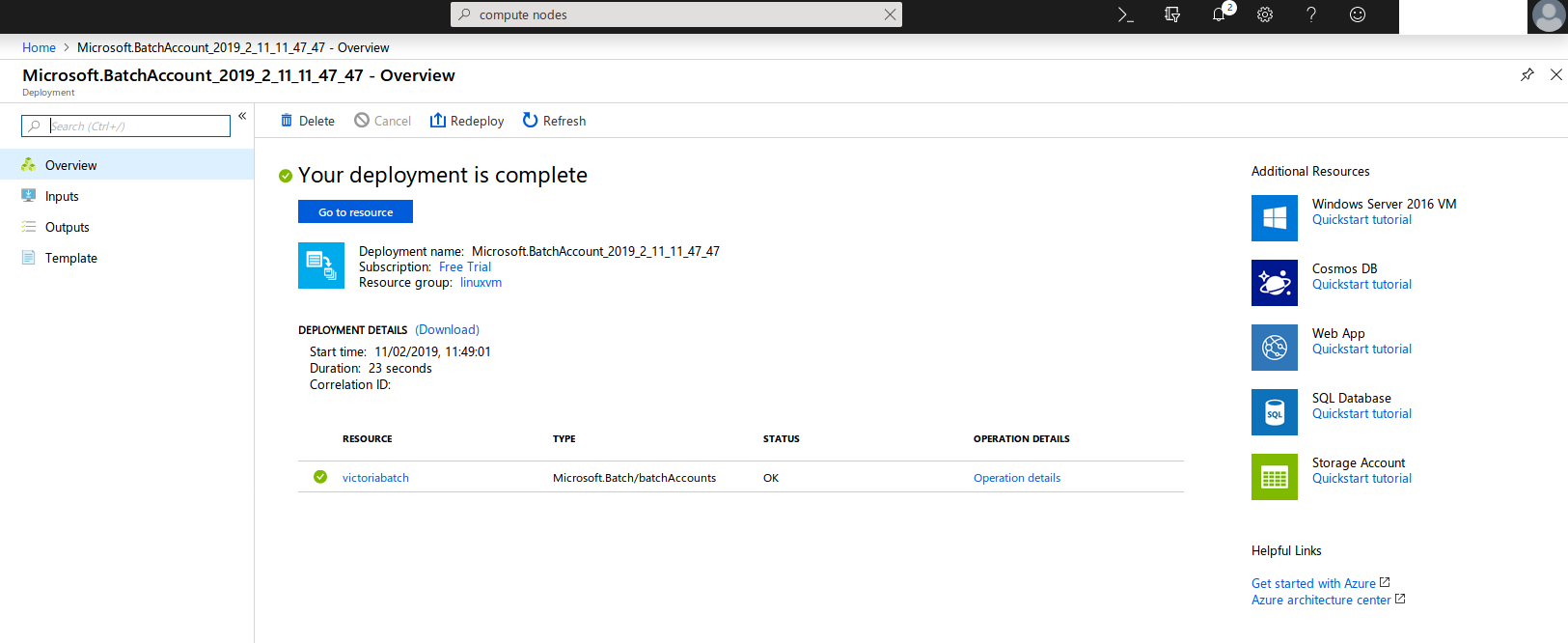
Once deployed, click Go to resource.
Click on Pools under Features.
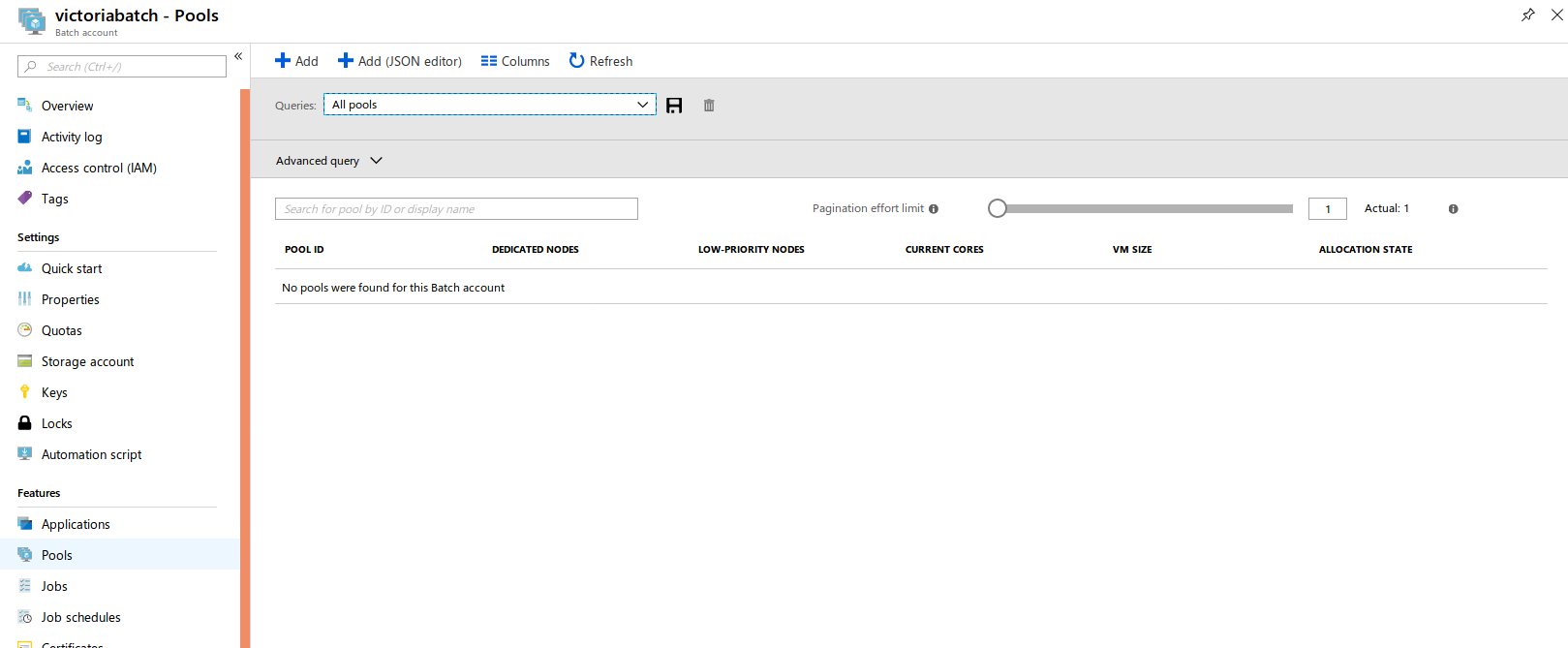
Click next. Create an ID name for Pool ID, select Canonical for Publisher, UbuntuServer for Offer, and 18.04-LTS for Sku.
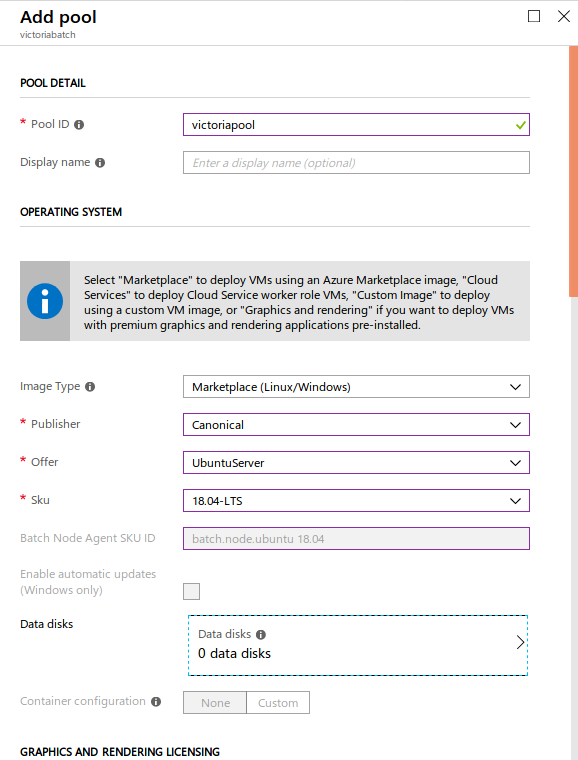
Scroll down. Select Standard A2 (2 Cores, 3.5 GB Memory) for VM size and 1 for Target dedicated nodes. Leave other options. Click OK. This may take a few minutes to Resize until the allocation state is Steady.
Now, click on Cloud Shell or the >_ symbol to launch the command line.
Now you are going to run a simple batch job!
Login to your batch account
az batch account login --name <your batch account name> --resource-group linuxvm --shared-key-auth
Create a job
az batch job create --id myjob --pool-id <your pool id>
Next, deploy a task where you print “Hello, world!”
az batch task create --task-id mytask --job-id myjob --command-line "/bin/bash -c 'echo Hello, world'"
Print the output of the file locations.
az batch task file list --job-id myjob --task-id mytask --output table
You should get something like this:

Download the output of the task.
az batch task file download --job-id myjob --task-id mytask --file-path stdout.txt --destination ./stdout.txt
Look at the contents of the file
cat stdout.txt

You can also run jobs in parallel. Here we run four jobs. This will run concurrently in batches of 2 (as we requested a pool of two cores). Each core can run one job. Here is a bash script that is running the command to print “Hello, world” and the task number.
first lets create your job code file.
cat > myArrayJob.sh
copy and past the code below and once complete choose CTRL + D
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..4}
do
az batch task create \
--task-id mytask$i \
--job-id myjob \
--command-line "/bin/bash -c 'echo Hello, world $i!'"
done
Set permission:
chmod 755 myArrayJob.sh
Execute script:
./myArrayJob.sh
Download output:
az batch task file download --job-id myjob --task-id mytask1 --file-path stdout.txt --destination ./stdout1.txt
Print output:
cat stdout1.txt
You can read more on how to create Batch jobs here.
License
Some material has been taken from Unix shell course under a CC-BY-NC-SA license.